Exploring Manufacturing 4.0 Part 3: Tailwinds & Emerging Technologies

Exploring Manufacturing 4.0 Part 3: Tailwinds & Emerging Technologies

Exploring Manufacturing 4.0 Part 3: Tailwinds & Emerging Technologies

Exploring Manufacturing 4.0 Part 3: Tailwinds & Emerging Technologies

Welcome back to the final part of our Manufacturing 4.0 series which sheds light on the transformative journey the manufacturing sector is undergoing right now.
A quick recap before we dive in - In Part 1, we explored the technological evolutions that have shaped this sector, emphasizing the role of Artificial Intelligence in modern manufacturing processes.
In Part 2, we did an in-depth analysis of the major categories and subcategories within this space, complemented by an overview of startup performance metrics, including funding rounds, successful exits, and revenue growth.
As we bring this series to a close, this final piece talks about the key tailwinds and emerging technologies poised to redefine the landscape of manufacturing.
Key Tailwinds
Manufacturing is a constantly evolving space that is being shaped by several key tailwinds that are accelerating the growth and adoption of various technologies. McKinsey has identified eight key value drivers that are indicative of the impact of digitization and Industry 4.0 technologies on a typical manufacturing company, as illustrated in the figure below.
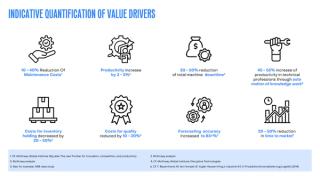
Here’s our view on the tailwinds that are currently shaping the future of manufacturing.
Advancements in Hardware (Sensors) and Software
- Computer Vision Reliability: The advancements in computer vision technology are a game-changer for quality control. Machines can now interpret visual data to identify defects or irregularities, thereby reducing human error and increasing throughput.
- Edge Computing: By processing data closer to its source, edge computing minimizes latency and enables real-time decision-making. It also improves data security, as most of the computing process takes place on premise.
Compliance and Security Regulations
- Data Privacy: Complying with stricter data privacy rules like GDPR requires companies to adopt digital systems for detailed record-keeping and consent logging. Although driven by regulation, this digitization gives manufacturers valuable production data. With better visibility through digital tracking, they can optimize efficiency, reduce defects, and make data-backed decisions. So ultimately, privacy compliance accelerates smart manufacturing, rather than just addressing legal risks.
- Electronic Record-Keeping and Traceability: Strict requirements for detailed electronic record-keeping and product traceability necessitate significant digitization efforts. As manufacturers adopt advanced databases and software platforms to capture production data, they also gain broader visibility into inefficiencies. With end-to-end digital tracking, manufacturers can closely monitor quality, optimize production planning, and make data-backed decisions to improve processes.
- Worker Safety and Health: Regulatory pushes from agencies like OSHA are driving the adoption of technologies that monitor and enhance worker safety, thereby reducing workplace accidents and preventing workers from long-term health effects.
- Environmental Sustainability: With an increasing focus towards sustainability, companies are looking for technologies that can provide them data-driven insights and offer them the capabilities to build tools that can minimize waste and optimize the use of energy.
Evolving Business Requirements
As businesses mature, their requirements and expectations from their technologies solution also change. In the Industry 4.0 era, key factors that businesses consider when adopting a new manufacturing technology include:
- Enhanced ROI via higher productivity
- Lower operating costs.
- Data connectivity, visibility, and control over processes.
- Integration of operations, analytics, and visualization tools.
- User-friendly setup and immediate operational value.
- Comprehensive coverage across the entire value chain.
- Robust security and governance measures.
- Advanced intelligence through machine learning-driven data insights and recommendations.
Favorable market conditions
Industry 4.0 is anticipated to catalyze productivity gains on a scale similar to the first industrial revolution. McKinsey's estimates suggest a global impact ranging from $1.2 to $3.7 trillion. Further analysis from the firm indicates significant productivity enhancements and Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE) improvements among early adopters in major industries.

Increase in adoption of new technologies through modern manufacturing equipment
All modern manufacturing equipment today ships with an array of IoT sensors, software packages, and other technologies. As companies replace old machinery with new, they naturally transition into the next era of manufacturing technology.
This transition gives them the power to create a network of connected devices through which they can monitor, optimize, and automate their manufacturing processes in real-time.
The widespread use of these technologies will actively improve the opportunities for startups that create solutions for the Manufacturing 4.0 sector.
Apart from the aforementioned technologies we discussed, there are few cutting edge areas that are drawing the attention of everyone in the manufacturing space. Let’s take a look at those.
Areas we are excited about

1. Digital Twin
Imagine having a virtual replica of your entire manufacturing plant. You can use it to simulate various scenarios, keep an eye on things in real-time, check for problems, and make predictions about what might happen next. This can help you work more efficiently and prepare you to face various unforeseen scenarios on the shop floor. Currently, digital twins are mostly used by manufacturers for downtime prediction and maintenance planning of machines, so they can lower maintenance times and subsequently improve productivity.
According to Gartner, the market size for digital is expected to reach a staggering $183 billion by 2031.
Companies like Siemens and GE are already leveraging digital twins to offer solutions to everything from product development to predictive maintenance. GE claims that they’ve saved $1.6 billion to date for their customers using digital twins.
According to their official website, GE has deployed over 1.2 million Digital Twins of jet engines, wind-farms, off-shore oil rigs, power generation equipment, pumps, compressors, chillers, and more.
2. Predictive Maintenance
The primary reason for revenue loss in manufacturing plants is the occurrence of operational downtime. According to Forbes, An average manufacturer faces 800 hours of equipment downtime per year. This results in several billion dollars worth of revenue lost.
The use of predictive maintenance technologies can help minimize these losses. Predictive maintenance involves the use of AI and ML to make accurate and timely maintenance predictions. AI-powered algorithms can now predict when a machine is likely to fail, allowing for timely interventions that save both time and money.
According to market research reports, the global predictive maintenance market is expected to grow from $4.0 billion in 2020 to $12.3 billion by 2025.
3. IoT PaaS
As manufacturers adopt more IoT-enabled devices, they are realizing many of these systems cannot communicate with each other due to different communication protocols, data schemas, velocities etc. IoT Platform as a Service (PaaS) serves as an integration layer to bridge this gap. IoT PaaS solutions provide pre-built interfaces that connect previously siloed manufacturing systems, machines, and data sources. This connectivity powers use cases like rapid reconfigurations, Over-the-Air updates, and unified data analytics.
According to Gartner’s forecast, The IoT PaaS market is expected to grow at 34% CAGR, creating a $33 billion market opportunity in 2025.
4. Cyber-Physical Systems Security
As manufacturing floors become increasingly populated by sensors, data flows, and connected equipment, protecting these cyber-physical production systems grows critical. The risks are real - vulnerabilities in unpatched firmware or unsecured test equipment could provide entry points for bad actors. Stolen operational data or manipulated machine instructions from compromised devices can severely hamper output.
Technical solutions that specifically address these issues have a huge growth opportunity. Startups in this space are already building solutions to detect network anomalies, fight malware, run integrity checks during machine-to-machine communication, identify and block unauthorized communication attempts across plant equipment, and so on.
According to a Zion market research study, the global Cyber-Physical Systems (CPS) Market is expected to grow from $76.98 Billion to $177.57 Billion at a 8.01% CAGR in 2023-2030.
5. Data Ops
Historically, production data has been gathered in siloed systems, limiting manufacturers from deriving holistic insights from their existing data. Data Ops solutions are here to change that. These solutions ingest data from multiple sources - equipment sensors, quality checks, inventory databases - and construct a unified data pipeline for better understanding.
Industrial leaders increasingly realize the potential of having a massive trove of operational data and are currently focused on efficiently gathering, organizing, and analyzing flows to optimize every manufacturing facet—from predictive maintenance to supply chain logistics. According to the DataOps Platform Market report, the Data Ops platform market is currently at $3.9 billion and is expected to reach over $10 billion by 2028.
Adjacent opportunities also emerge in industrial data monetization. As regulatory compliance tightens and stakeholders demand sustainability insights, Data-as-a-Service offerings provide value. Subject matter experts package niche production telemetry into risk assessments, environmental impact reports, and operational benchmarks. This enables data-backed decision-making for manufacturers and partners.
6. Defect Detection
Legacy defect detection methods struggle to catch issues in real-time during production. But with computer vision and deep learning based defect detection systems, manufacturers now spot defects and irregularities with increased speed and accuracy.
Beyond rapid surface-level image scans, these systems are capable of advanced simulation techniques like 3D modeling and ultrasonic monitoring that allow more rigorous non-destructive testing. These create multidimensional analysis of possible flaws in components like welds or casts at early stages.
According to KBV Research’s report, The defect detection market is expected to grow over 7% annually to $5 billion by 2026. The market will see a lot of competition in the coming years as adjacent market players are already venturing into this space.
This doesn’t mean the market is too saturated. Startups that are focusing explicitly on machine learning for manufacturing inspection like Landing.AI and Cogniac are making rapid strides in this space.
With more companies venturing into this space, the future looks promising - one where every manufactured part gets thoroughly evaluated for minute defects without slowing cycle times or requiring vast manual approval.
7. Telematics
The field of Telematics is revolutionizing how fleet operators manage and oversee their vehicles.
Electronic Logging Devices (ELDs) make it easier for fleet managers and drivers to keep track of their Hours of Service (HOS), manage the driver vehicle inspection records (DVIR) and perform International Fuel Tax Agreement (IFTA) reporting.
This tech helps keep tabs on driver safety and also leads to smarter fuel use, minimizes accidents, and lessens the risk of injury claims.
In a significant move, the Federal Motor Carrier Safety Administration (FMCSA) made it compulsory in December 2015 for commercial trucks and buses to have ELDs installed in them.
This step towards adopting telematics widely marks a shift towards more efficient, safe, and cost-effective fleet management, indicating a future where logistics operations are more streamlined and technologically driven.
8. Supply Chain Traceability
Businesses across different industries are seeking solutions to enhance visibility into their supply chain processes, aiming to boost transparency with their customers, partners, and stakeholders. Stricter regulatory requirements, heightened consumer and investor expectations, and technological advancements are driving this change.
Industries focused on perishable goods, healthcare products and services, luxury brands, and consumer electronics are more likely to adopt solutions in this space.
The critical goal here is to establish proof of origin to guard against counterfeits and ensure traceability of the product journey for regulatory and compliance purposes.
Additionally, companies are exploring ways to personalize products based on local consumer preferences, achievable only through advanced traceability.
This evolution towards more transparent and responsive supply chain practices marks a significant step toward ensuring safety, authenticity of goods, compliance, and consumer satisfaction.
The future looks promising
The future of Manufacturing 4.0 is not just promising; it's downright exhilarating. As we stand on the cusp of another industrial revolution, the possibilities are endless. If you are building or working in any of the above spaces, we’d love to chat more! Get in touch with us at saas@elevationcapital.com.
Written by Poorvi Vijay
Related

Vridhi: Reimagining Home Lending For Bharat's Self-Employed
Ram Naresh Sunku, Co-founder, Vridhi Home Finance
11.12.2024

Investing in Plena Data
Automating manual accounting tasks and improving employee experience with robots
14.10.2021

Monetization Strategies That Work: Insights from Consumer Tech Founders
Insights on what works when it comes to monetizing consumer apps in India.
10.12.2024